Menu
- Solutions
- Videos
- Industries
- Software
- Support
- Careers
- Company
- Contact
3DCS Variation Analyst software provides users with a variety of methods to solve problems in assembly and manufacturing. These include:
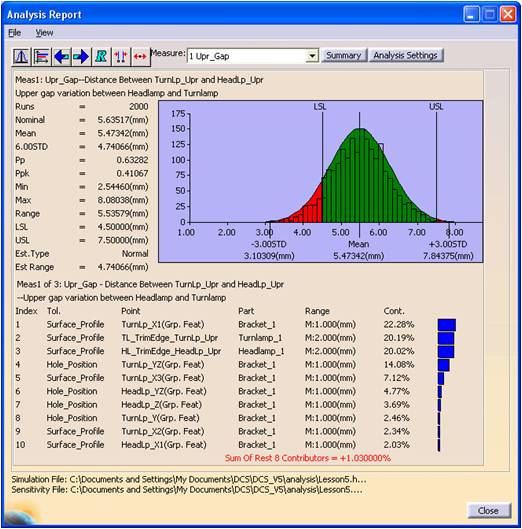 3DCS is most often used to predict the risk of failure early in the digital phase. By using Monte Carlo simulation to create virtual measurements, 3DCS allows for statistical analysis of multiple thousands of product builds, determining critical, and non-critical, areas of concern as well as the risk of non-conformance. By acting on these results, engineers can make iterative changes to tolerances and the design in order to control variation, and set up inspection to catch outliers by monitoring critical areas of the assembly. This process produces robust designs with less risk of failure and reduces scrap, rework, and time to market.
3DCS is most often used to predict the risk of failure early in the digital phase. By using Monte Carlo simulation to create virtual measurements, 3DCS allows for statistical analysis of multiple thousands of product builds, determining critical, and non-critical, areas of concern as well as the risk of non-conformance. By acting on these results, engineers can make iterative changes to tolerances and the design in order to control variation, and set up inspection to catch outliers by monitoring critical areas of the assembly. This process produces robust designs with less risk of failure and reduces scrap, rework, and time to market.
A Digital Twin is a model that accurately represents the physical product. In manufacturing, this requires GD&T and tolerances, as the nominal build will never behave or represent actual manufactured parts that vary in size, shape, and thickness. 3DCS adds another layer to your model in CAD by meshing over the parts and accurately simulating the true dimensions of your parts. This allows engineers to create more accurate models and better see the effects of variation on assembly processes and product performance.
 Closed Loop Manufacturing and Problem Solving involve feedback loops in the product lifecycle that continually feed data upstream to provide engineers the ability to improve the design as production continues. Additionally, this allows engineers to validate their design and compare their simulation results to as-measured parts in the plant in order to update their predictive models (Digital Twin) to more accurately represent their true product. In doing so, they are able to validate the parts and process, and better predict issues that may occur.
Closed Loop Manufacturing and Problem Solving involve feedback loops in the product lifecycle that continually feed data upstream to provide engineers the ability to improve the design as production continues. Additionally, this allows engineers to validate their design and compare their simulation results to as-measured parts in the plant in order to update their predictive models (Digital Twin) to more accurately represent their true product. In doing so, they are able to validate the parts and process, and better predict issues that may occur.
With the ability to utilize measured data in an analysis model, replacing tolerance ranges with as-measured production data, engineers can use their CAD model with 3DCS to accurately find the source of problems in production. If there are unexpected assembly problems, gap issues, flush conditions, functional problems, the Digital Twin can be used to find the contributors to the problem, and hone in on possible solutions. These solutions can then be tested digitally before being rolled out, confirming their effectiveness and removing the need for trial and error.
Download the article presented in Quality Magazine titles 'Closed Loop Manufacturing: CAD Driven Supplier Quality' to learn more about the use of 3DCS to drive quality downstream and reduce costs across the entire product lifecycle.