EMBRAER Dimensional Management Process
Product Development -- Measurement and Simulation
Determine the requirements to be measured early. 3DCS simulations help to integrate product development and accelerate maturity.
Manufacturing -- Make or Buy
Most important is to get the requirements that were simulated and apply them to update the drawings. Using this strategy to drive processes and controls.
Manufacturing Quality -- Process Control
The goal is to improve manufacturing quality by applying the tolerances to the drawings and validating the parts.
Assembly -- Assembly Process
Assemblies and Sub-assemblies must have requirements and tolerances. Datum are the main output for tooling and assembly process.
Assembly Quality -- Process Control
The focus is to anticipate the detection of potential problems in one step, thus minimizing their effects on the rest of the production chain.
Embraer - Working With Large Models - Black Box Methodology
Luiz Marcelo Ventorini, Mechanical Engineer, has been working as a Dimensional Engineer since 2006 in Product Development, performing Tolerance Analysis for several kinds of requirements (Aerodynamics, Stress, Systems and Manufacturing), GD&T applications and Interface Control Documents (with suppliers). He has also been working in the prototype and series phases activities such as product validation (metrology) and analyzing the difficulties faced on the assembly line.
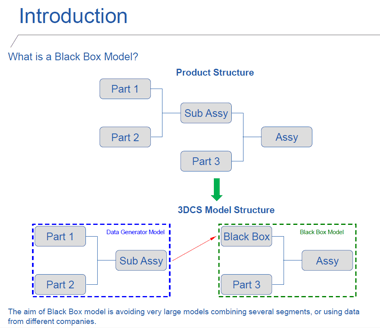
As an aerospace engineer, Marcelo Ventorini often deals with extremely large models which can make analysis time consuming and slow. To speed up his analysis, Ventorini utilizes a technique called the 'Black Box Methodology'.
Black Box Methodology aims to turn sub-assemblies into single components when working in a model. By analyzing the sub-assembly first, the variation from that assembly can be applied to the overall assembly as a component in a larger structure, such as an aircraft.
This also helps when using data from suppliers, and in the case of 3DCS users, when using parts that may contain Compliant Components. Once the sub-assembly is black boxed, it contains the variation from its own analysis, but does not bog down your overall tolerance analysis simulation. This also removes the need to continually use Add-on module licenses when opening the model.
Advantages of Black Box:
- A big model with a lot of MTMs and a big stackup can be replaced by some points and tolerances;
- Only final results can be shared with other companies. Modeling strategy and process tolerances are hidden;
- Several Black Box Scenarios can be done based on only one model Data Generator Model run;
- Heavy FEA Compliant models can be replaced by a few points (also optimizing FEA licenses).
Disadvantages of Black Box:
- Depending on the result some curve fit must be done and some errors are generated;
- Some local datums must be created to measure the specific relationship between features;
- The original model is split, it’s necessary to manage two models;
- Some tricky higher order interaction, if not detected, can be lost;
- On the black box model, the sensitivity doesn't show the contributors (they are all bundled).
Learn more about Black Box Methodology in the DCS Webinar on how to use this technique