Add Finite Element Analysis to your tolerance analysis system
Traditional variation analysis methods are considered to be "rigid-body" or "non-compliant" modeling; meaning, that every part within the assembly does not flex or would not be distorted through an assembly process such as welding, clamping or unclamping of an assembly fixture.
While this might be the case with a few machined components, most commodities and materials like sheet metal, plastics, aluminum, etc. can be heavily influenced through the manufacturing processes (both fabrication and assembly), thus changing the dimensional integrity or shape of the part/assembly. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is used to determine the stresses and displacements in mechanical objects and systems, and is the basis for this leading edge advancement in predictive analysis.
3DCS FEA Compliant Modeler, an add-on module to the 3DCS software solutions, utilizes FEA methods to accurately simulate variation of compliant parts and assemblies within the 3D Variation Analysis model.
Combine traditional tolerance analysis with FEA analysis to determine the impact of clamping, force, gravity and heat on your parts
When welding, bolting, riveting or assembling parts, the order and the process can have as much of an effect on final results as the parts themselves. Riveting can stretch aircraft aluminum skin, assembling can bend and cause spring back, and bolting can warp materials. Simulate, test and determine the best order of operations and the impact these processes will have on your parts.
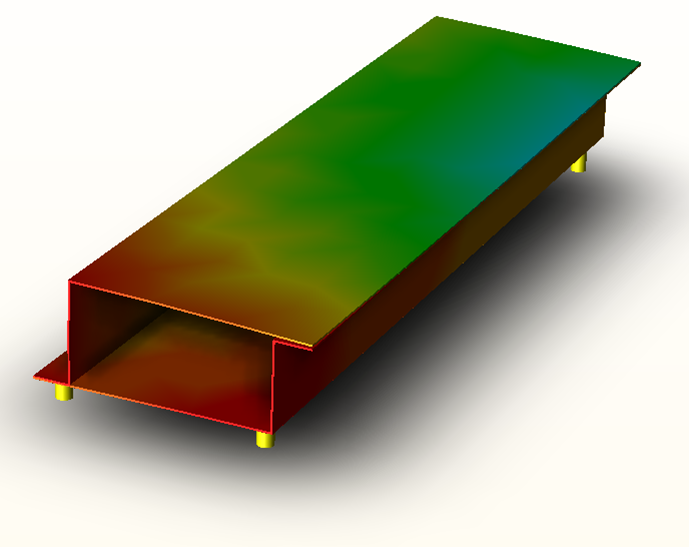
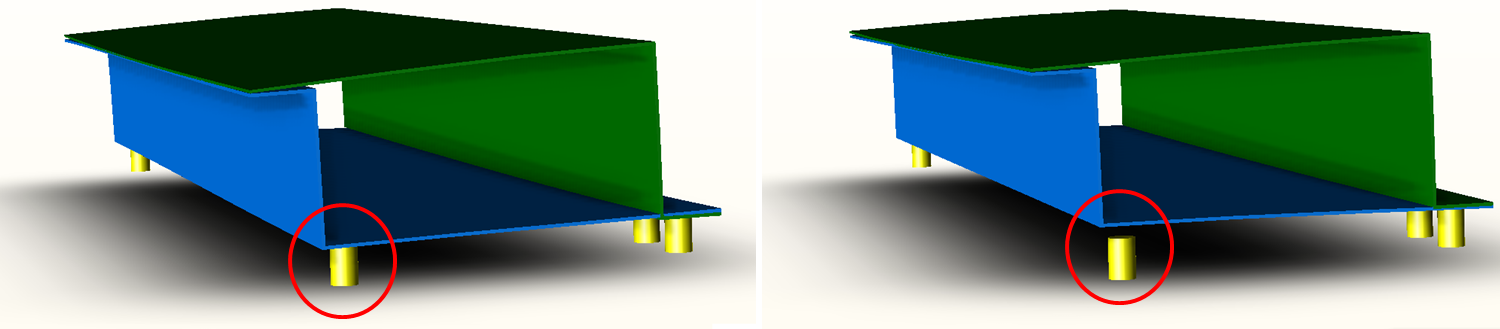
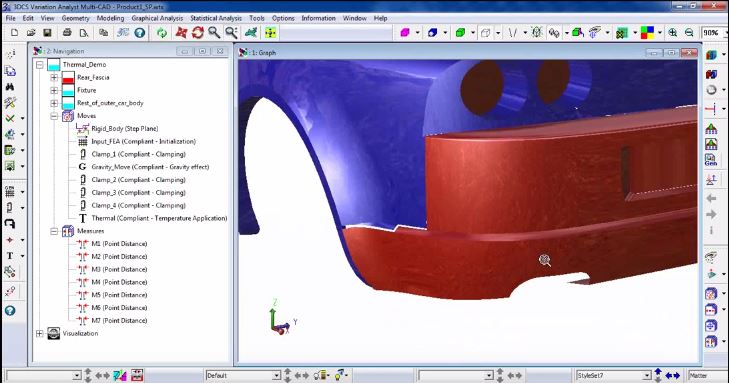
Analyze the effects of processes like welding, clamping or the release of tooling. Use Finite Element Analysis to accurately predict the material response to forces and heat.
Determine the changes to your product based on constraints, forces and operations.
Test different assembly sequences and processes such as welding, riveting, bolting and clamping to find optimal placements, order of operation and the effect on the assembly.
Determine how welding, bolting and connecting parts affects the dimensional characteristics of your product. Find out how the use of flexible materials like aluminum changes the way your product reacts to manufacturing processes.
Parts sag from their weight, or expand when welded or in use. Automotive hoods flex and bend to product springback force, and aluminum skin in aircraft stretches and distorts when riveted. Determine how these processes and forces affect your product's quality, and account for it through process change, tolerance changes or tooling.
Interested in seeing for yourself? Fill out the form below to get a free demonstration of 3DCS FEA Compliant Modeler.
DCS will never share your information with a third party or add you to a mailing list without permission. Read our privacy policy to learn more about how DCS protects your information.
DCS Global Headquarters
2805 Bellingham Dr
Troy, Michigan, 48083
Phone: 1.248.269.9777
Fax: 1.248.269.9770
Website: www.3dcs.com
Email: sales@3dcs.com